Prevention of Cervical Cancer
Prevention of Cervical Cancer
Most cervical cancers can be prevented. There are 2 ways to prevent this disease. The first way is to find and treat pre-cancers before they become cervical cancer, and the second is to prevent the occurrence of cervical pre-cancer.
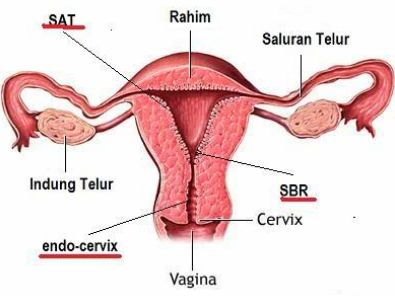
Pap Smear Test: named according to its inventor, Dr. George Papanicolaou (1883-1962) of Greece. This test is used to reveal whether there is infection, inflammation, or abnormal cells in the cervix (neck of the womb).
Pap smear test can be performed in hospitals, clinics or laboratories nearest obstetrician. The procedure is quick (only takes a few minutes) and painless.
Pap smear test can be done when you are not in a state of menstruation or pregnancy. For best results, you should not have sex at least 3 days before the examination.
Figure 1: The doctor inserts (tool) speculum into the vagina to hold the vaginal walls open.
Figure 2: Liquid / cervical mucus is taken by rubbing (tool) spatula.
Figure 3: The swab was then applied to the object-glass
Figure 4: The sample is ready to be brought to the pathology laboratory for examination.
Type of Test Pap Smear:
Conventional Pap smear test
As the picture above.
Thin prep Pap.
Usually done when the results of the conventional Pap smear test is not good / obscure. Mucus samples were taken with a special tool (cervical brush), not with a wooden spatula and the results are not added to the object-glass, but sprayed with a special liquid to separate contaminants, such as blood and mucus so that the results more accurate.
Thin prep plus HPV DNA test
Done when the Pap smear test results is less good. Samples examined whether HPV DNA.
GUIDELINES FOR EARLY DETECTION Cervical Cancer:
The women should begin Pap smear test about 3 years after they started having sex, but not older than age 21 years.
Testing should be done every year if the regular Pap smear tests are used, or every 2 years if liquid-based Pap test used.
Starting at age 30, women who have a NORMAL test results as much as 3x in a row may be able to undergo a Pap smear test every 2 to 3 years. Another option for women over 30's is undergoing a Pap smear test every 3 years plus the HPV DNA test.
Women who have certain risk factors (such as HIV infection or have a weak immunity) should get a Pap smear every year.
Women aged 70 years or older with Normal Pap test results for 3 years in a row (and had no abnormal test results in the last 10 years) may choose to stop doing Pap smear test this. But women who had cervical cancer or who have other risk factors (as mentioned above) should continue to pull through this test as long as they are in good health.
Women who had undergone total hysterectomy may also choose to stop doing Pap test unless it has undergone surgery to treat cervical cancer or pre-cancer. Women who had undergone a simple hysterectomy (cervix is not removed) must still follow the guidelines above.
Some women believe that they can stop doing Pap smear tests after they stop having children. This is not true. They should continue to follow the guidelines above.
Pelvic examination vs. Pap Smear Test
Many people are often confused between a pelvic examination vs. Pap smear tests, perhaps because both of these things are often done at the same time. Pelvic exam is part of a woman's routine health care. During this examination, the doctor may see and feel the reproductive organs. Some women think that they do not need a pelvic exam after they stop having children. This is not true.
Pelvic exams can help find diseases of the female organs. But it's not going to find cervical cancer at an early stage. For that, the Pap smear test is required. Pap smear test is often done just before the pelvic examination.
Another alternative Pap Smear Tests: Methods IVA
For early detection of cervical cancer, in addition to the Pap smear test, other methods which may be an option is the VIA (Visual Inspection with Acetic Acid).
IVA is used to detect abnormalities in your cervical cells after applying acetic acid solution (cuka3 acid-5%) of the cervix. Acetic acid confirm and mark the pre-cancerous lesions with somewhat whitish discoloration (acetowhite change). The result can be known right away, or within 15 minutes.
IVA method contains an advantage over a Pap smear test, because it is very simple (can be done in the PHC), the result is quite sensitive and very affordable prices (from USD. 5000).
Unlike the Pap smear test, examination method IVA can also be done anytime, including during menstruation, during childbirth or post-abortion care. If the result is nice, visit VIA test is repeated for every 5 years.
Images: Various VIA test results
[...]
Most cervical cancers can be prevented. There are 2 ways to prevent this disease. The first way is to find and treat pre-cancers before they become cervical cancer, and the second is to prevent the occurrence of cervical pre-cancer.
Pap Smear Test: named according to its inventor, Dr. George Papanicolaou (1883-1962) of Greece. This test is used to reveal whether there is infection, inflammation, or abnormal cells in the cervix (neck of the womb).
Pap smear test can be performed in hospitals, clinics or laboratories nearest obstetrician. The procedure is quick (only takes a few minutes) and painless.
Pap smear test can be done when you are not in a state of menstruation or pregnancy. For best results, you should not have sex at least 3 days before the examination.
Figure 1: The doctor inserts (tool) speculum into the vagina to hold the vaginal walls open.
Figure 2: Liquid / cervical mucus is taken by rubbing (tool) spatula.
Figure 3: The swab was then applied to the object-glass
Figure 4: The sample is ready to be brought to the pathology laboratory for examination.
Type of Test Pap Smear:
Conventional Pap smear test
As the picture above.
Thin prep Pap.
Usually done when the results of the conventional Pap smear test is not good / obscure. Mucus samples were taken with a special tool (cervical brush), not with a wooden spatula and the results are not added to the object-glass, but sprayed with a special liquid to separate contaminants, such as blood and mucus so that the results more accurate.
Thin prep plus HPV DNA test
Done when the Pap smear test results is less good. Samples examined whether HPV DNA.
GUIDELINES FOR EARLY DETECTION Cervical Cancer:
The women should begin Pap smear test about 3 years after they started having sex, but not older than age 21 years.
Testing should be done every year if the regular Pap smear tests are used, or every 2 years if liquid-based Pap test used.
Starting at age 30, women who have a NORMAL test results as much as 3x in a row may be able to undergo a Pap smear test every 2 to 3 years. Another option for women over 30's is undergoing a Pap smear test every 3 years plus the HPV DNA test.
Women who have certain risk factors (such as HIV infection or have a weak immunity) should get a Pap smear every year.
Women aged 70 years or older with Normal Pap test results for 3 years in a row (and had no abnormal test results in the last 10 years) may choose to stop doing Pap smear test this. But women who had cervical cancer or who have other risk factors (as mentioned above) should continue to pull through this test as long as they are in good health.
Women who had undergone total hysterectomy may also choose to stop doing Pap test unless it has undergone surgery to treat cervical cancer or pre-cancer. Women who had undergone a simple hysterectomy (cervix is not removed) must still follow the guidelines above.
Some women believe that they can stop doing Pap smear tests after they stop having children. This is not true. They should continue to follow the guidelines above.
Pelvic examination vs. Pap Smear Test
Many people are often confused between a pelvic examination vs. Pap smear tests, perhaps because both of these things are often done at the same time. Pelvic exam is part of a woman's routine health care. During this examination, the doctor may see and feel the reproductive organs. Some women think that they do not need a pelvic exam after they stop having children. This is not true.
Pelvic exams can help find diseases of the female organs. But it's not going to find cervical cancer at an early stage. For that, the Pap smear test is required. Pap smear test is often done just before the pelvic examination.
Another alternative Pap Smear Tests: Methods IVA
For early detection of cervical cancer, in addition to the Pap smear test, other methods which may be an option is the VIA (Visual Inspection with Acetic Acid).
IVA is used to detect abnormalities in your cervical cells after applying acetic acid solution (cuka3 acid-5%) of the cervix. Acetic acid confirm and mark the pre-cancerous lesions with somewhat whitish discoloration (acetowhite change). The result can be known right away, or within 15 minutes.
IVA method contains an advantage over a Pap smear test, because it is very simple (can be done in the PHC), the result is quite sensitive and very affordable prices (from USD. 5000).
Unlike the Pap smear test, examination method IVA can also be done anytime, including during menstruation, during childbirth or post-abortion care. If the result is nice, visit VIA test is repeated for every 5 years.
Images: Various VIA test results